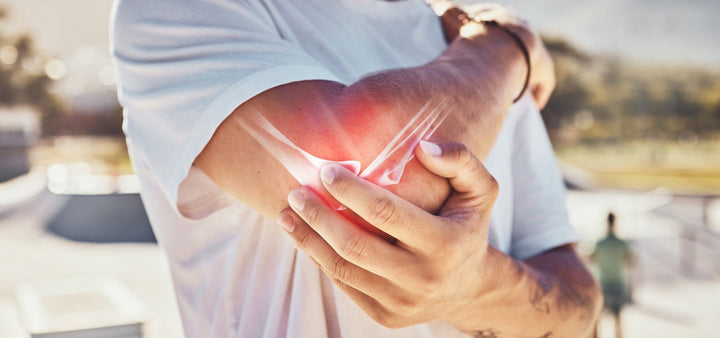
What is Glucosamine?
Glucosamine is an amino sugar found naturally in the body, particularly in joint cartilage — the tough, flexible tissue that cushions bones and helps support smooth movement. As we age, the body's natural production of glucosamine may decrease, which is why supplements have become a popular choice to maintain joint health as part of a balanced lifestyle.
Why Take Glucosamine?
Glucosamine supplements are widely used by people who want to:
- Support the maintenance of normal cartilage and joint structure
- Maintain flexibility and mobility over time
- Look after their joint health during ageing or physical activity
- Complement their overall wellness routine
There are no major food sources of glucosamine, so supplementation is often the most practical way to obtain it.
Types of Glucosamine Supplements
Glucosamine Hydrochloride (HCl)
A highly concentrated, well-absorbed form of glucosamine. Often preferred for its purity and suitability in plant-based formulations. It contains a greater proportion of active glucosamine per gram than the sulphate form.
Glucosamine Sulphate (2KCl)
A widely studied version of glucosamine, commonly combined with potassium chloride to enhance stability. Traditionally derived from shellfish, but alternative sources are becoming available.
Glucosamine Complexes
Many products combine glucosamine with other ingredients commonly used for joint support, including:
- Chondroitin sulphate – a naturally occurring component of cartilage
- Boswellia extract – traditionally used for joint comfort
- Turmeric extract (Curcuma longa) – valued for its antioxidant properties
- MSM (methylsulfonylmethane) – a source of sulphur, included in many joint formulations
- L-Methionine and Quercetin – amino acids and plant flavonoids often included in advanced complexes
Choosing the Right Glucosamine Supplement
When selecting a glucosamine supplement, it helps to consider:
- Form: HCl vs Sulphate
- Source: Plant-based or shellfish-derived
- Added ingredients: Chondroitin, turmeric, MSM, vitamin C, etc.
- Format: Capsules vs tablets
- Daily dosage: Typically ranges from 500 mg to 1500 mg per day
Each product page provides full ingredient details and usage recommendations to help you decide.
Plant-Based Glucosamine Options
While many traditional glucosamine supplements are derived from shellfish, there are also plant-based alternatives available. These are typically produced through the fermentation of non-GMO corn and are commonly used in formulations designed for those avoiding animal products or shellfish.
Plant-based glucosamine is often found in hydrochloride (HCl) form and may be preferred by individuals with dietary restrictions or allergies. However, it's important to review full product ingredient lists, as not all supplements using plant-based glucosamine are necessarily suitable for vegans or vegetarians.
Who Might Choose Glucosamine?
- Adults over 40 supporting long-term joint health
- Physically active individuals, including gym-goers and athletes
- People with physically demanding lifestyles
- Those looking to maintain mobility as they age
- Customers seeking high-quality joint supplements made in the UK
Frequently Asked Questions
Is glucosamine suitable for long‑term use?
Yes, glucosamine is commonly taken as part of a long‑term wellness routine.
Can I take glucosamine with other supplements?
Yes, it’s often combined with turmeric, collagen, or omega 3. If you’re taking medication, consult a healthcare professional.
What’s the difference between HCl and Sulphate?
Glucosamine HCl contains more active glucosamine per gram and is often preferred in plant‑based supplements. Sulphate is more widely studied and traditionally used.
Is this supplement suitable for people with shellfish allergies?
Some formulations use plant‑based glucosamine, but we recommend checking the full ingredient list and consulting your doctor if you have allergies.
How should I take glucosamine?
Take as directed on the product label — usually 1 to 2 capsules per day with food.
How long does it take to see effects?
Some users choose to take glucosamine daily over several weeks as part of their joint care routine, though individual results may vary.
Can I take glucosamine during pregnancy, breastfeeding or with medication?
If you're pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking medication, it’s best to consult your healthcare professional before starting glucosamine, as it may interact with certain treatments.
Are there any side effects from taking glucosamine?
Glucosamine is generally well tolerated. Some people report mild effects such as bloating, nausea, or diarrhea. If symptoms persist, stop use and consult a healthcare professional.
Does glucosamine interact with medications like warfarin?
Glucosamine may enhance the effect of blood-thinning medication such as warfarin, increasing bleeding risk. If you're on such medications, check with your doctor before use.
*Food supplements should not be used as a substitute for a varied and balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. This information is for educational purposes and is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Always consult your healthcare professional before taking any supplement, especially if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, taking medication, or under medical supervision.